Failure in Monocrystalline Silicon Differential Pressure Sensor
During the measurement process, there are often some failure to monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensors for some reason. Timely analysis and processing for the failure is critical to ongoing production. Monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensors have high stability, low temperature drift and high accuracy. However, industrial site conditions are often complex and harsh. The strong corrosiveness and strong electromagnetic interference of the application environment is a severe test for the normal operation of the differential pressure sensor. Therefore, based on practical experience, this paper summarizes the failure and the corresponding treatment methods for monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensors.
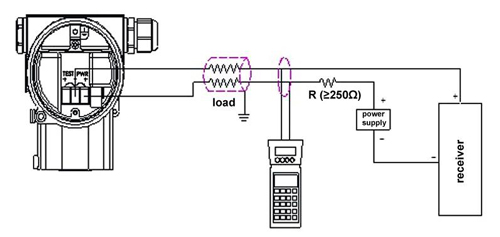
There are roughly several reasons for this.

II. The output of monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensor is low
The reason and treatment are as follows.
The reason is that the flow in the process line is unstable. Identify the specific cause and eliminate unstable flow.
V. The output of the monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensor exceeds the maximum value
The reason is that the flow maximum exceeds the range of the flowmeter. Stop the flowmeter to understand production load and material balance.
VI. The output of monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensor is high
- Circuit failure of monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensor
- Pressure pipe failure of the monocrystalline differential pressure sensor
- Electromagnetic field interference around the installation position of monocrystalline pressure sensor
- High voltage pipe and low voltage pipe connection for monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensor is reversed
- The root valve of the orifice plate or the positive and negative pressure valve at the top of the sensor are not opened. Check the pressure line and open the valve of the positive and negative pressure line.
- The balancing valve is not closed. The balancing valve should be closed at this time.
- A leak occurs at the joint of the positive pressure line.
- The output of the monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensor is abnormal
There are roughly several reasons for this.
- No power or poor power contact. Check the power circuit and power supply.
- Poor contact or disconnection in the signal line. Check the output line to resolve the problem.

II. The output of monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensor is low
The reason and treatment are as follows.
- The balancing valve is not closed. Close the balancing valve.
- There are leaks on the positive pressure side pipelines, valves, etc. Check the leak point on the positive pressure side and do the leak prevention work.
- The valve on the positive pressure side is not open. Open the valve on the positive pressure side.
- When there is a liquid column in the pressure line, there is gas in the positive pressure tube or the positive pressure chamber of the monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensor, or the liquid column is lower than the liquid column in the negative pressure tube. Drain the pressure sensor or treat the liquid columns in the positive and negative pressure tubes to maintain the same height.
The reason is that the flow in the process line is unstable. Identify the specific cause and eliminate unstable flow.
V. The output of the monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensor exceeds the maximum value
The reason is that the flow maximum exceeds the range of the flowmeter. Stop the flowmeter to understand production load and material balance.
VI. The output of monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensor is high
- There are leakage in pipelines, valves, etc. on the negative pressure side. Check and handle leaks.
- When there is a liquid column in the pressure line, there is gas in the negative pressure tube or the negative pressure chamber of the monocrystalline silicon differential pressure sensor, or the liquid column is lower than the liquid column in the positive pressure tube. Drain the sensor or treat the liquid columns in the positive and negative pressure tubes to maintain the same height. It is also possible to open a large negative pressure side valve, handle blowdown, and the like.

