What is Pressure Sensor Zero Drift
The zero drift of the pressure sensor refers to the phenomenon that when the amplifier input is short-circuited, an irregular, slowly changing voltage is generated at the output. The main cause of zero drift is the effect of temperature changes on transistor parameters and fluctuations in supply voltage. In most amplifiers, the zero drift in the front stage has the greatest influence. The more the stages number and the larger the magnification, the more serious the zero drift.
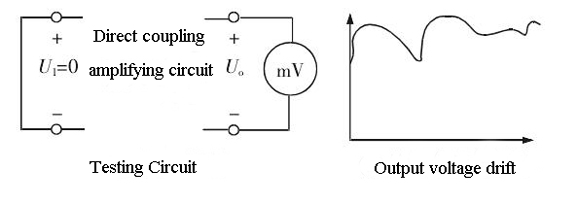
The zero drift of the pressure sensor refers to the phenomenon that when the input pressure is zero, the output value jumps forward, negative or up and down with time in the specified test conditions. In order to prevent moisture, rain, and harmful gases, the circuit board of the pressure sensor is designed and manufactured in a sealed structure. If the case and the hex lock nut are not tightened, the normal working conditions of the electronic circuit will be destroyed. As a result, the pressure sensor is exposed to moisture, rain, and harmful gases, resulting in a decrease in insulation performance or corrosion of the electronic components, causing a drift in the pressure sensor output value. The unstable pressure sensor output will directly affect the operation of the measurement and control system.
The size of the drift is mainly due to the selection of strained materials. The structure or composition of the material determines the heat sensitivity or stability of the pressure sensor. It is also important to manufacture after selecting the material. Different process will produce strain values with different effect. The key is also the stability or regular change of the bridge value after some aging and other adjustments.
In addition, improper use can also cause the zero drift of the pressure sensor, summed up the following.
The change in output value due to changes in the ambient temperature of the pressure sensor is called the pressure sensor temperature error. Any change in value that meets the technical standards is a normal change. The temperature coefficient given in the operating instructions of the pressure sensor means that when the temperature coefficient of the adjusted range is calculated in the high range, the coefficient is multiplied by the range ratio (the ratio of the highest range to the adjusted range). The pressure sensor models and specifications are different, so the temperature coefficient are different. Within the normal range of output value in morning, noon, evening at site, in which the normal zero should change regularly. This change is especially noticeable at the scene with large temperature differences and low-range pressure sensors, as long as they do not exceed the standard.
The output change due to static pressure that meets the technical standards is also a normal change. Especially for the pressure sensor with small range, because of the large conversion magnification, the output value caused by static pressure changes greatly. The key is to see if there is any technical standard. The point is to see if it exceeds technical standard.
- The pressure sensor zero drift concept

The zero drift of the pressure sensor refers to the phenomenon that when the input pressure is zero, the output value jumps forward, negative or up and down with time in the specified test conditions. In order to prevent moisture, rain, and harmful gases, the circuit board of the pressure sensor is designed and manufactured in a sealed structure. If the case and the hex lock nut are not tightened, the normal working conditions of the electronic circuit will be destroyed. As a result, the pressure sensor is exposed to moisture, rain, and harmful gases, resulting in a decrease in insulation performance or corrosion of the electronic components, causing a drift in the pressure sensor output value. The unstable pressure sensor output will directly affect the operation of the measurement and control system.
- The pressure sensor zero drift reason
The size of the drift is mainly due to the selection of strained materials. The structure or composition of the material determines the heat sensitivity or stability of the pressure sensor. It is also important to manufacture after selecting the material. Different process will produce strain values with different effect. The key is also the stability or regular change of the bridge value after some aging and other adjustments.
In addition, improper use can also cause the zero drift of the pressure sensor, summed up the following.
- The primary component (orifice plate, remote measurement connector, etc.) is blocked or installed in a wrong form, and the position of the pressure tapping point is unreasonable.
- There is leakage or blockage in the pressure guiding tube; residual gas in the liquid filling tube or residual liquid in the inflation tube; deposits in the sensor, forming a dead zone.
- Sensor wiring is incorrect, power supply voltage is too high or too low; poor contact at the connection between the meter head and the meter terminal.
- The installation is not strictly in accordance with the technical requirements, and the installation method and the on-site environment do not meet the technical requirements.
- Situation that allow zero drift
The change in output value due to changes in the ambient temperature of the pressure sensor is called the pressure sensor temperature error. Any change in value that meets the technical standards is a normal change. The temperature coefficient given in the operating instructions of the pressure sensor means that when the temperature coefficient of the adjusted range is calculated in the high range, the coefficient is multiplied by the range ratio (the ratio of the highest range to the adjusted range). The pressure sensor models and specifications are different, so the temperature coefficient are different. Within the normal range of output value in morning, noon, evening at site, in which the normal zero should change regularly. This change is especially noticeable at the scene with large temperature differences and low-range pressure sensors, as long as they do not exceed the standard.
The output change due to static pressure that meets the technical standards is also a normal change. Especially for the pressure sensor with small range, because of the large conversion magnification, the output value caused by static pressure changes greatly. The key is to see if there is any technical standard. The point is to see if it exceeds technical standard.

